WHAT IS APICAL RESECTION?
When root canal treatment fails, inflammatory areas or cysts may occur at the ends of the tooth roots due to various reasons. In order for the patient to be treated without losing a tooth, the
diseased tissue at the root tip is cut and removed. This method is called Apical Resection.
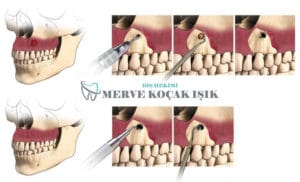
Root canal treatment can fail for a variety of reasons. The most common cause of failure is due to overflow of root canal treatment. Not all teeth have the same morphological structure, some tooth roots may contain various lateral canals, and it is not possible to reach these canals with traditional methods.
When root canal treatment fails, problems such as infection, pain, swelling and fistula formation will occur at the root tip. Sometimes they appear as apical cysts that manifest themselves radiologically without causing any discomfort to the patient. In such cases, only the use of antibiotics is not a definitive solution, but also paves the way for the problem to recur in the long run. The reason for this is that the causative agent of the infection has not been removed. Extraction is an option when root canal treatment fails. A prosthesis or implant to replace the missing tooth makes the treatment more costly. Although it is possible to make prostheses as comfortable as natural teeth, thanks to advanced technology, the first goal of dentistry is not to lose natural teeth. The other option other than pulling the tooth is apical resection, this method is to reach the root tip by lifting the flap under local anesthesia, and after the diseased tissue is removed with some root tip, the root canal is cleaned and filled again, depending on the size of the cavity formed, the use of bone graft may be required.
In studies on the success of apical resection cases, a success rate of 97% to 99% has been determined.
It is a preferred method to prevent tooth loss in appropriate indications.
